Software Engineering
Software Engineering is a discipline within computer science that focuses on the systematic design, development, testing, and maintenance of software systems. It encompasses a set of principles, methodologies, and practices aimed at producing high-quality software that meets user needs efficiently and reliably.
Some key aspects of software engineering:
-
Requirements Analysis:
- Gathering and documenting user and system requirements.
- Defining the functional and non-functional requirements of the software.
- Ensuring that the software aligns with the needs and goals of stakeholders.
-
System Design:
- Creating a high-level architectural design for the software.
- Decomposing the system into modules or components.
- Defining the data structures and algorithms to be used.
- Considering scalability, performance, and security aspects.
-
Coding and Implementation:
- Writing code in accordance with design specifications.
- Adhering to coding standards and best practices.
- Employing appropriate programming languages and development tools.
- Collaborating with team members through version control systems.
-
Testing:
- Conducting various levels of testing, including unit testing, integration testing, and system testing.
- Identifying and fixing defects and issues.
- Ensuring the software meets functional and non-functional requirements.
- Performing regression testing to validate changes.
-
Documentation:
- Creating comprehensive documentation for the software, including user manuals and technical documentation.
- Maintaining up-to-date documentation throughout the software's lifecycle.
-
Quality Assurance:
- Implementing quality assurance practices to ensure the software is reliable and performs as expected.
- Conducting code reviews and inspections.
- Employing automated testing tools and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
-
Project Management:
- Planning and scheduling software development projects.
- Managing resources, timelines, and budgets.
- Identifying and mitigating risks.
- Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban are often used for project management.
-
Maintenance and Support:
- Providing ongoing maintenance and support for software in production.
- Monitoring and addressing issues and bugs.
- Making updates and enhancements based on user feedback and changing requirements.
-
Security:
- Implementing security best practices to protect the software from vulnerabilities and threats.
- Conducting security assessments and audits.
- Ensuring data privacy and compliance with relevant regulations.
-
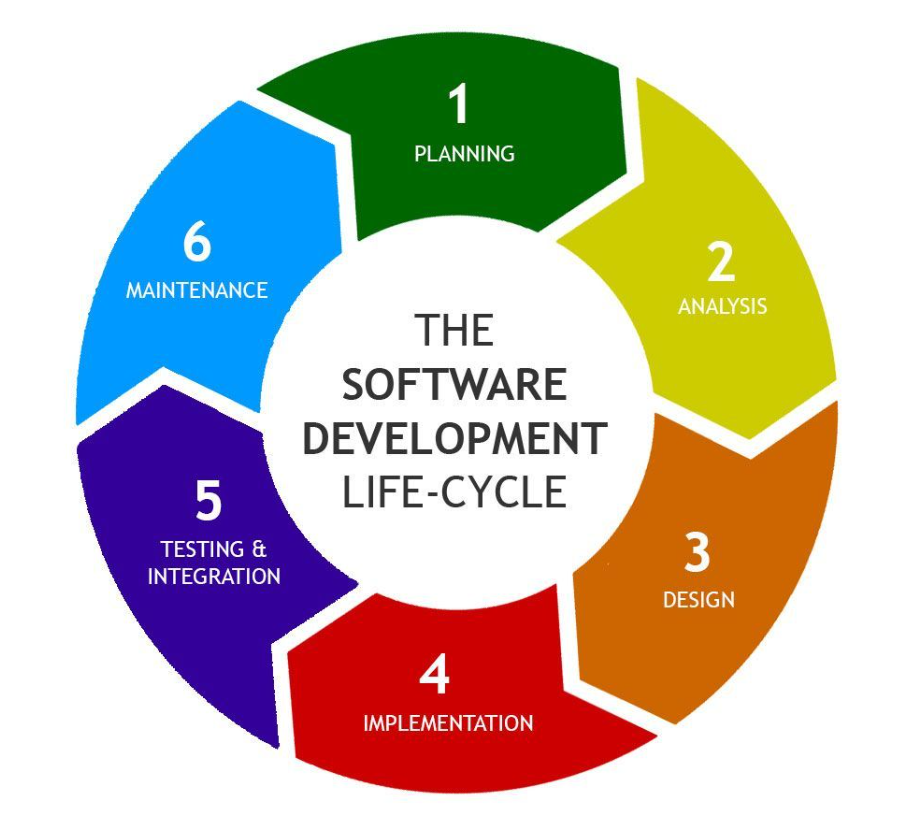
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC):
- Following a structured SDLC, which may include waterfall, Agile, or hybrid approaches.
- Iteratively developing and releasing software to accommodate changing requirements.
-
Ethical and Professional Considerations:
- Adhering to ethical standards and legal obligations.
- Promoting responsible and ethical use of technology.
- Continuing education and professional development.
-
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design:
- Creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
- Conducting usability testing and gathering user feedback for iterative design improvements.
Software engineering is a dynamic field that continues to evolve with advancements in technology and changing user needs. It plays a crucial role in building software systems that power a wide range of applications, from mobile apps and web services to embedded systems and large-scale enterprise applications. Effective software engineering practices are essential for delivering reliable, secure, and maintainable software solutions.