Python Programming
Introduction
Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language. It is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, and is used for a wide variety of applications, including web development, data science, and machine learning. Python is a very easy language to learn. It has a simple syntax that is similar to English, and it has a large community of users and developers who are always willing to help.
Variables
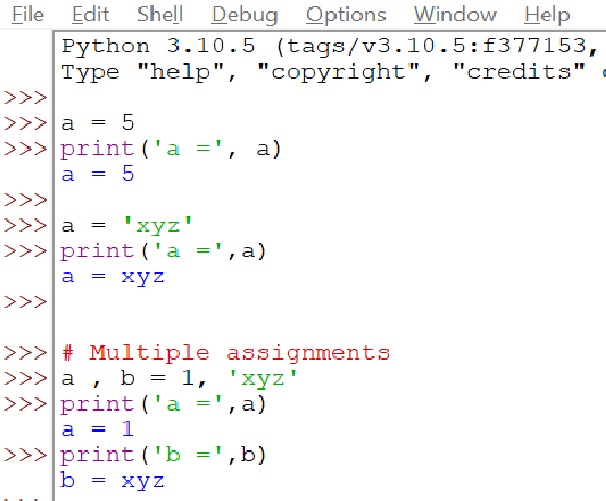
Variables are used to store data in Python. Variables can be assigned any type of data, including strings, integers, floats, and lists. To declare a variable, you use the var_name = value syntax. For example, the following code declares a variable named x and assigns it the value 10:
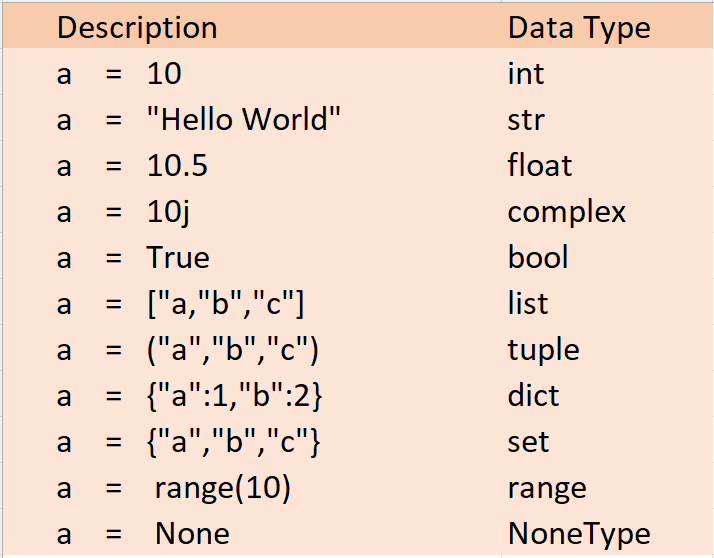
Python has a number of different data types. The most common data types are:
Strings: Strings are sequences of characters.
Integers: Integers are whole numbers.
Floats: Floats are numbers with decimal points.
Lists: Lists are sequences of objects.
Operators
Python has a number of operators that can be used to perform operations on data.
The most common operators are:
Arithmetic operators: These operators are used to perform arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Comparison operators: These operators are used to compare two values. Logical operators: These operators are used to combine logical expressions.
Control flow statements
Control flow statements are used to control the flow of execution of a Python program.
The most common control flow statements are:
if statements: if statements are used to execute code if a certain condition is met.
for loops: for loops are used to execute code repeatedly, for each item in a sequence.
while loops: while loops are used to execute code repeatedly, while a certain condition is met.
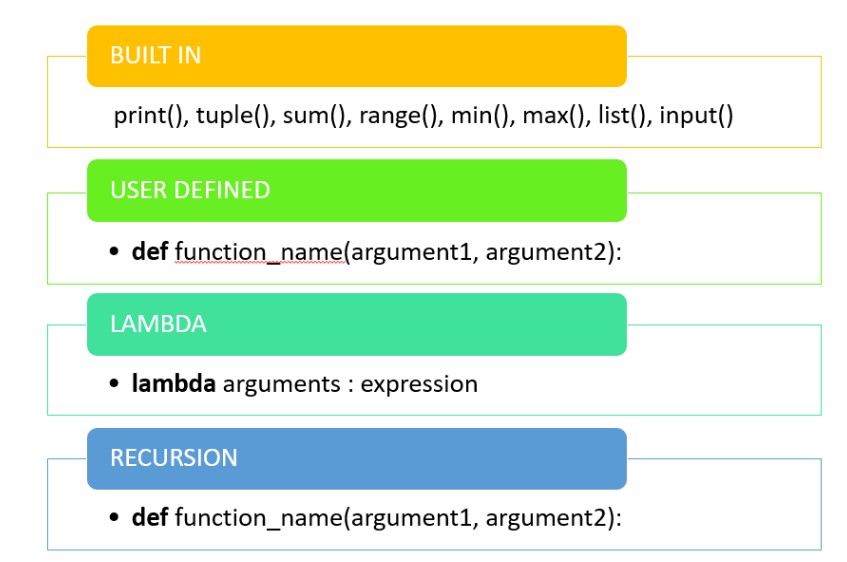
Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code. Functions can be used to encapsulate code and make it easier to read and maintain. To define a function, you use the def keyword.
For example, the following code defines a function named my_function
Modules
Modules are files that contain Python code. Modules can be used to organize code and make it easier to reuse. To import a module, you use the import keyword.
For example, the following code imports the math module: import math
Classes
Classes are used to create custom data types. Classes can be used to encapsulate data and behavior, and to make code more reusable. To define a class, you use the class keyword.
For example, the following code defines a class named MyClass:
Object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that uses objects to represent data and behavior. OOP is a very powerful programming paradigm, and it is used by many popular programming languages, including Python.
History of Python Programming Language
1. Creation and Development (Late 1980s - Early 1990s):
- 1980s: Guido van Rossum, a Dutch programmer, began working on Python as a hobby project.
- December 1989: Van Rossum started the implementation of Python.
- February 1991: The first version (0.9.0) was released to the public on alt.sources. It included functions, exception handling, and the core data types (list, dict, str, etc.).
2. Python 1.x (1994 - 2000):
- January 1994: Python 1.0 was released. It included new features such as lambda, map, filter, and reduce.
- October 2000: Python 1.6 was released with features like Unicode support.
3. Python 2.x (2000 - 2010):
- October 2000: Python 2.0 was released. Key features included list comprehensions, a garbage collector for cyclic references, and support for Unicode.
- December 2008: Python 2.6 was released, introducing some features from Python 3.0 to ease the transition.
4. Python 3.x (2008 - Present):
- December 2008: Python 3.0 (also known as "Python 3000" and "Py3k") was released. It was designed to rectify fundamental design flaws in the language. Notably, it is not backward compatible with Python 2.x.
- Key Changes in Python 3.0:
- Print is now a function, not a statement.
- Integer division returns a float (e.g., 5/2 = 2.5).
- Text and data are explicitly distinct types (str for Unicode text, bytes for binary data).
- The
xrange()function was removed in favor of a reworkedrange()function.
- Key Changes in Python 3.0:
5. Python's Popularity and Ecosystem Growth:
- 2010s: Python's popularity surged due to its readability, simplicity, and the rise of data science, machine learning, and web development.
- Scientific Computing: Libraries like NumPy, SciPy, pandas, and Matplotlib became foundational for scientific research and data analysis.
- Web Development: Frameworks such as Django and Flask gained popularity for web development.
- Machine Learning and AI: Libraries like TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch made Python the go-to language for AI research and development.
6. Python 2 End of Life:
- January 1, 2020: Python 2 reached its end of life, and the Python Software Foundation officially stopped supporting it. Users were encouraged to transition to Python 3.
7. Current and Future Developments:
- Continued Evolution: Python continues to evolve with new releases that add features and improvements, maintaining its reputation for readability and ease of use.
- Widespread Use: Python is now a dominant language in various fields including web development, data science, automation, artificial intelligence, and more.
Key Features and Philosophy
- Readability: Emphasizes code readability and simplicity.
- Dynamically Typed: Supports dynamic typing and automatic memory management.
- Interpreted Language: Python code is executed line-by-line, which makes debugging easier.
- Extensive Libraries: A vast standard library and an active community contribute to numerous third-party packages.
- Cross-Platform: Python runs on various platforms including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Python Community and Governance
- Open Source: Python is an open-source language, maintained by the Python Software Foundation.
- PEP (Python Enhancement Proposal): PEPs are design documents providing information to the Python community or describing new features for Python or its processes.
Python's growth and adoption over the years highlight its significance in the programming world, making it a versatile and powerful language for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion This is just a brief introduction to Python. There is much more to learn about this powerful programming language. I encourage you to explore the Python documentation and to learn more about Python by reading books, articles, and tutorials.
Enroll Now- Python Programming
- Machine Learning