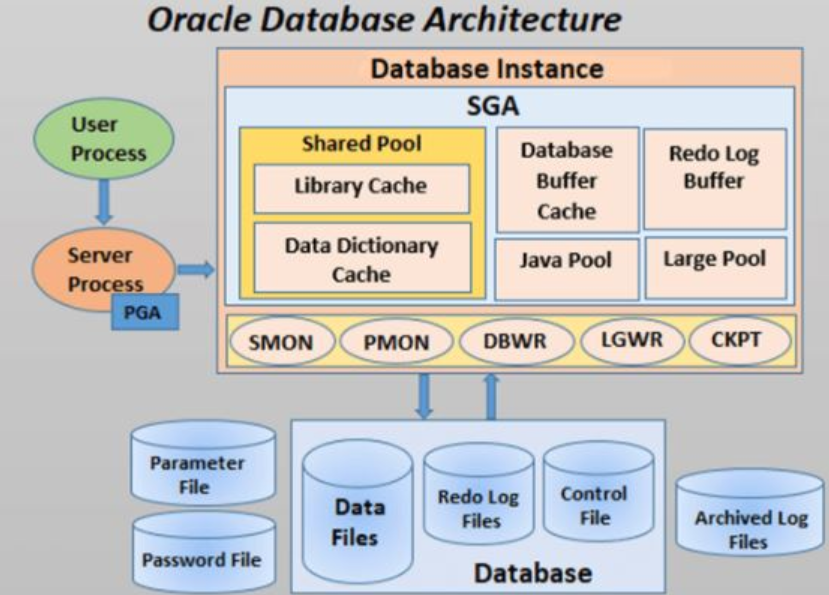
Oracle Database administration
Oracle Database administration involves the tasks and responsibilities associated with managing, maintaining, and optimizing an Oracle Database to ensure its reliability, security, and performance.
The role of an Oracle Database administrator (DBA) is critical in supporting the organization's data infrastructure and ensuring that the database operates efficiently and meets business requirements.
Some key aspects of Oracle Database administration:
-
Installation and Configuration: The DBA is responsible for installing and setting up Oracle Database software on servers or cloud instances. This includes configuring various parameters, such as memory allocation, database storage, and network settings.
-
Backup and Recovery: Ensuring the database's data is regularly backed up and can be restored in case of data loss or corruption is essential. DBAs set up backup strategies, perform backups, and conduct recovery operations when necessary.
-
Performance Monitoring and Tuning: DBAs continuously monitor the database's performance to identify bottlenecks, optimize SQL queries, tune database parameters, and improve overall system responsiveness.
-
Security Management: Oracle Database administrators enforce security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. This involves managing user accounts, access privileges, and implementing encryption and auditing as needed.
-
Database Upgrades and Patching: DBAs plan and execute database upgrades to newer versions and apply patches to address security vulnerabilities and bug fixes.
-
Capacity Planning: DBAs analyze the database usage trends to forecast future resource requirements and plan for database growth accordingly.
-
High Availability and Disaster Recovery: Implementing technologies like Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC), Data Guard, and Flashback helps achieve high availability and disaster recovery capabilities for critical databases.
-
Database Schema Design and Management: DBAs collaborate with developers and data analysts to design efficient database schemas, create tables, indexes, and manage database objects.
-
Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution: When problems arise, DBAs investigate and resolve database issues promptly, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
-
Data Migration: Migrating data from one database to another (e.g., from development to production) or from legacy systems to Oracle Database requires careful planning and execution by the DBA.
-
Automation and Scripting: DBAs often write scripts and implement automation to streamline routine tasks and reduce manual effort.
-
Monitoring and Reporting: DBAs use monitoring tools to track database health, generate performance reports, and proactively address potential issues.
Oracle Database administration demands a deep understanding of Oracle technologies, database architecture, and best practices.
Continuous learning and keeping up with Oracle's latest features and updates are essential for a successful DBA career.
Additionally, Oracle offers certification programs for Database Administrators, helping them validate their expertise and stay competitive in the job market.