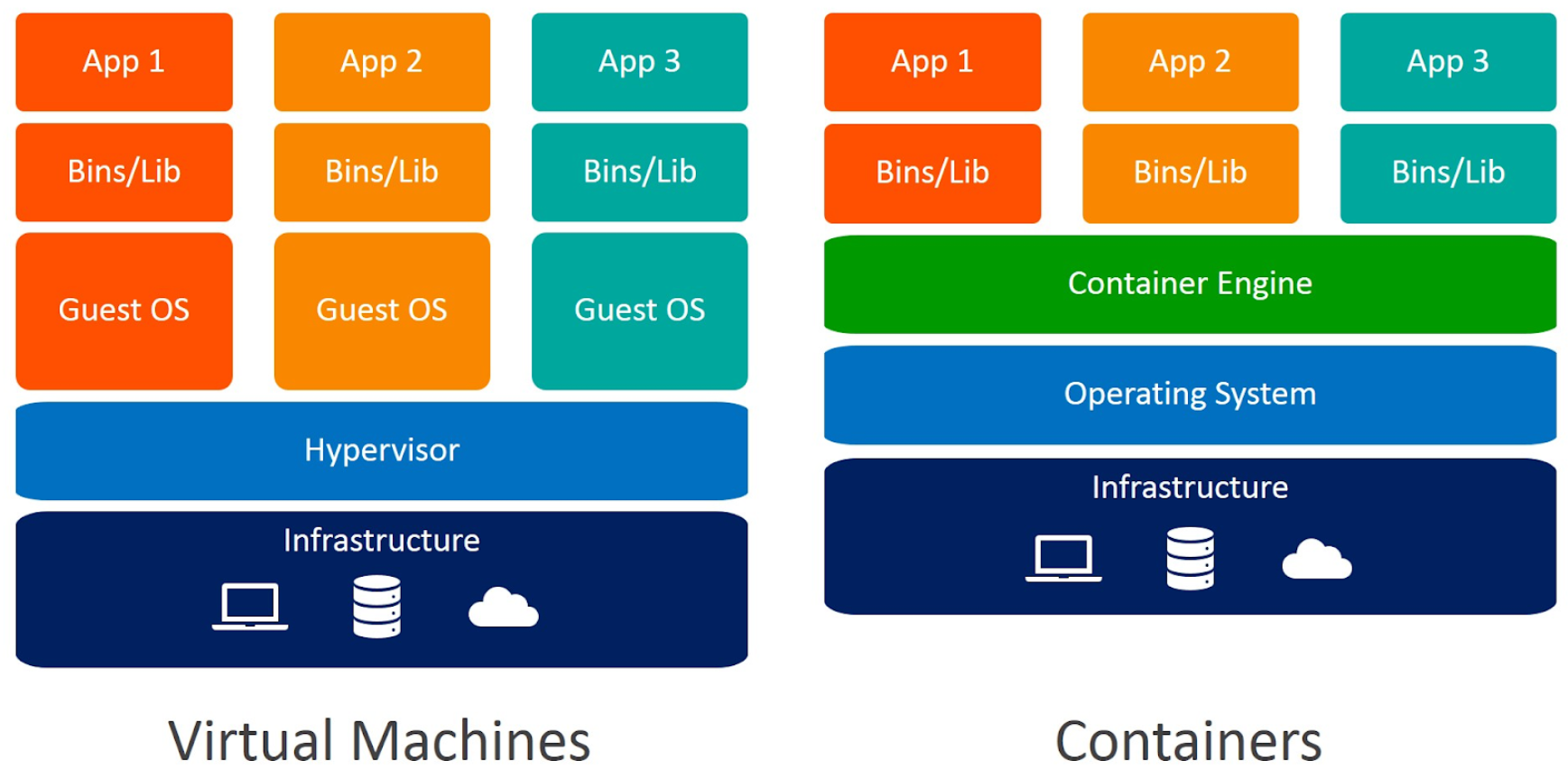
Docker Useful Commands
Docker is a widely used containerization platform, and there are several essential commands you can use to interact with Docker.
Docker commands:
-
Managing Containers:
docker run <image>: Create and start a new container based on an image.docker ps: List running containers.docker ps -a: List all containers (including stopped ones).docker start <container>: Start a stopped container.docker stop <container>: Stop a running container.docker restart <container>: Restart a container.docker rm <container>: Remove a stopped container.docker rm -f <container>: Forcefully remove a running container.
-
Managing Images:
docker pull <image>: Download an image from a registry.docker images: List locally available images.docker rmi <image>: Remove an image.docker build -t <image-name> <path-to-dockerfile>: Build a Docker image from a Dockerfile.docker tag <source-image> <target-image>: Tag an image to give it a new name and optional tag.docker push <image>: Push an image to a container registry.
-
Viewing Logs and Inspecting Containers:
docker logs <container>: View the logs of a container.docker inspect <container>: Retrieve detailed information about a container.
-
Managing Networks:
docker network ls: List Docker networks.docker network create <network-name>: Create a new Docker network.docker network connect <network> <container>: Connect a container to a network.docker network disconnect <network> <container>: Disconnect a container from a network.
-
Managing Volumes:
docker volume ls: List Docker volumes.docker volume create <volume-name>: Create a Docker volume.docker volume rm <volume-name>: Remove a Docker volume.
-
Managing Docker Compose:
docker-compose up: Start services defined in adocker-compose.ymlfile.docker-compose down: Stop and remove containers defined in adocker-compose.ymlfile.docker-compose logs: View logs of services in adocker-compose.ymlfile.docker-compose ps: List services and their status in adocker-compose.ymlfile.
-
Executing Commands Inside Containers:
docker exec -it <container> <command>: Run a command inside a running container interactively.
-
Container Statistics:
docker stats: Monitor container resource usage (CPU, memory, etc.) in real-time.
-
System Information:
docker info: Display system-wide information about Docker.docker version: Show the Docker version information.
-
Cleaning Up:
docker system prune: Remove all unused containers, networks, volumes, and images not referenced by any container.
These are some of the fundamental Docker commands to get you started. Docker offers many more commands and options for advanced use cases, so refer to the official Docker documentation for more information and examples.
Here are some useful Docker commands:
- docker version: Displays the current version of Docker.
- docker search <image name>: Searches for Docker images on Docker Hub.
- docker pull <image name>: Pulls a Docker image from Docker Hub to your local machine.
- docker run <image name>: Creates and runs a Docker container from the specified image.
- docker ps: Lists all running Docker containers.
- docker ps -a: Lists all Docker containers, including running, stopped, and exited containers.
- docker exec <container ID> <command>: Executes a command in the specified Docker container.
- docker stop <container ID>: Stops the specified Docker container.
- docker restart <container ID>: Restarts the specified Docker container.
- docker kill <container ID>: Forcefully kills the specified Docker container.
- docker rm <container ID>: Removes the specified Docker container.
- docker rmi <image name>: Removes the specified Docker image from your local machine.
- docker build -t <image name> <path to Dockerfile>: Builds a Docker image from the specified Dockerfile.
- docker push <image name>: Pushes the specified Docker image to Docker Hub.
These are just a few of the many useful Docker commands. For more information, please see the Docker documentation:
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/cli/
Here are some examples of how to use Docker commands:
- To pull the latest version of the Ubuntu image from Docker Hub:
docker pull ubuntu
- To run a container from the Ubuntu image:
docker run ubuntu
- To execute the
lscommand in the Ubuntu container:
docker exec $(docker ps -l -q) ls
- To stop the Ubuntu container:
docker stop $(docker ps -l -q)
- To remove the Ubuntu container:
docker rm $(docker ps -l -q)
- To build a Docker image from a Dockerfile:
docker build -t my-image .
- To push the
my-imageimage to Docker Hub:
docker push my-image
Docker is a powerful tool for containerizing applications. By learning the basic Docker commands, you can start to use Docker to streamline your development and deployment workflows.