Git Tutorial
Git is a widely used distributed version control system (DVCS) that plays a crucial role in modern software development.
It was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 and has since become the de facto standard for version control in the development industry.
Git provides a robust and efficient way to manage source code, track changes, collaborate with teams, and maintain the history of a project.
Overview of Git and its key concepts:
1. Distributed Version Control:
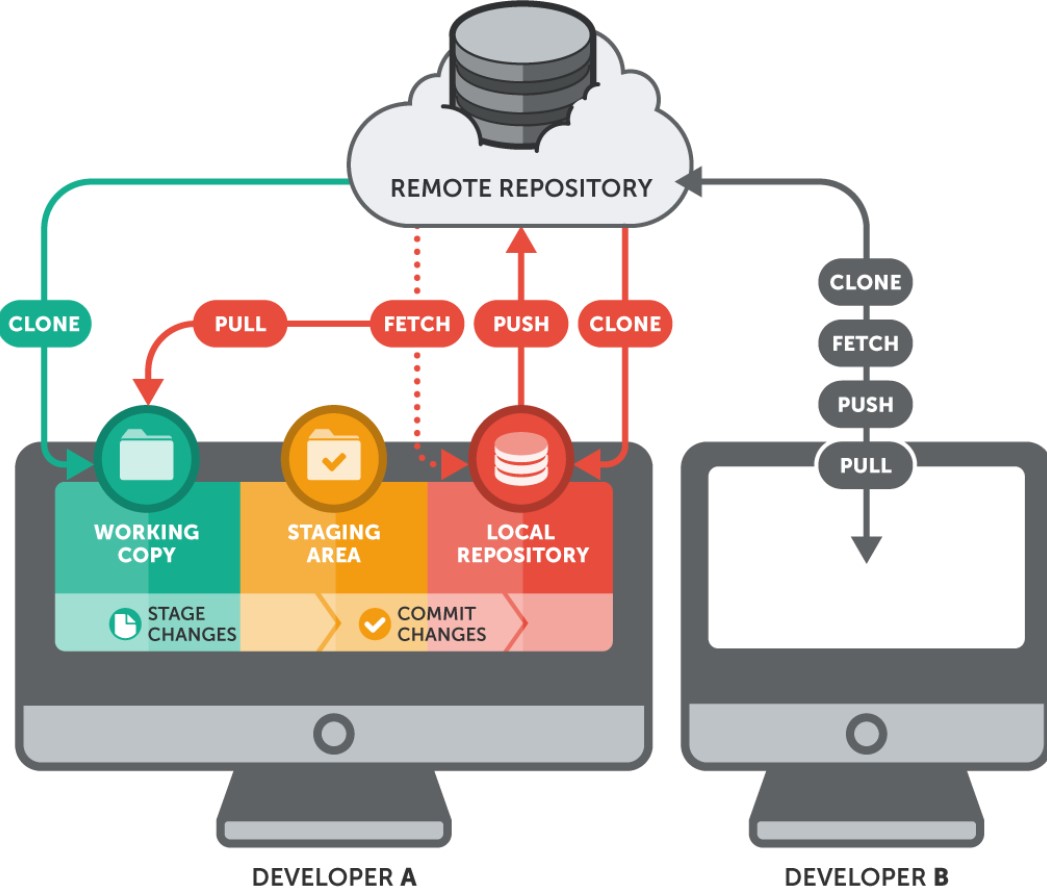
- Git is a distributed version control system, meaning that each developer has a complete copy of the entire repository, including its history. This decentralization allows for offline work and robust collaboration.
2. Repository (Repo):
- A Git repository is a directory that contains all the files, folders, and historical data for a project. It includes the source code and the entire history of changes made to the project.
3. Commit:
- A commit is a snapshot of the project at a particular point in time. It represents a set of changes made to the codebase. Commits are identified by unique hashes, and they include the author's name, email, timestamp, and a commit message describing the changes.
4. Branch:
- A branch is a parallel line of development within a Git repository. It allows multiple developers to work on different features or fixes simultaneously without affecting the main codebase. Branches can be created, merged, and deleted as needed.
5. Merge:
- Merging is the process of integrating changes from one branch (source branch) into another (target branch). This combines the changes and histories of both branches, creating a single branch with the merged changes.
6. Pull Request (PR) or Merge Request (MR):
- A pull request (in platforms like GitHub) or a merge request (in GitLab) is a mechanism for proposing and discussing changes to a Git repository. It allows developers to review and approve code changes before they are merged into the main branch.
7. Clone:
- Cloning is the process of creating a copy of a remote Git repository on your local machine. It downloads the entire repository, including its history, allowing you to work on the code locally.
8. Remote Repository:
- A remote repository is a Git repository hosted on a server or a cloud-based platform (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket). Developers can push their local changes to a remote repository and collaborate with others.
9. Fetch:
- Fetching is the process of updating your local repository with changes from a remote repository. It downloads new commits and branches without making any changes to your working directory.
10. Pull: - Pulling is a combination of fetching and merging. It fetches changes from a remote repository and automatically merges them into your current branch.
11. Push: - Pushing is the process of uploading your local commits to a remote repository. It updates the remote repository with your changes, making them available to other team members.
12. Version Control: - Git provides version control capabilities that allow developers to track and manage changes over time. This enables developers to revert to previous versions of the code, compare changes, and understand who made what changes and when.
13. Staging Area (Index): - Git uses a staging area or index to allow developers to selectively choose which changes to commit. This adds a level of granularity and control to the commit process.
14. Git Branching Strategies: - Git supports various branching strategies, such as feature branching, release branching, and git flow, to help teams manage code development and releases effectively.
15. Git Hooks: - Git hooks are scripts that can be triggered at specific points in the Git workflow. Developers can use hooks to automate tasks like code linting, testing, or triggering a build process.
Git's flexibility, speed, and robust branching and merging capabilities make it a powerful tool for version control and collaboration in software development.
It is widely adopted across the industry and serves as the foundation for many other DevOps and CI/CD practices and tools.