Java Variables
In Java, variables are used to store data values. They play a fundamental role in programming by allowing you to store and manipulate data within your programs. Java variables can hold various types of data, including numbers, text, and more complex objects.
Some key concepts related to Java variables:
- Integer Variables:
int age; // Declaration
age = 25; // Initialization
int anotherAge = 30; // Declaration and initialization
int sum = age + anotherAge; // Using in an expression
System.out.println("The sum of ages is: " + sum);
- String Variables:
String name; // Declaration
name = "Alice"; // Initialization
String greeting = "Hello, " + name; // Concatenating strings
System.out.println(greeting);
- Floating-Point Variables:
double salary; // Declaration
salary = 55000.75; // Initialization
double bonus = 5000.25;
double totalIncome = salary + bonus; // Using in an expression
System.out.println("Total income: $" + totalIncome);
- Character Variables:
char grade = 'A'; // Declaration and initialization with a character
char symbol = 65; // Initialization with Unicode value ('A' has Unicode value 65)
System.out.println("Grade: " + grade);
System.out.println("Symbol: " + symbol);
- Boolean Variables:
boolean isJavaFun = true; // Declaration and initialization
boolean isPythonFun = false;
System.out.println("Is Java fun? " + isJavaFun);
System.out.println("Is Python fun? " + isPythonFun);
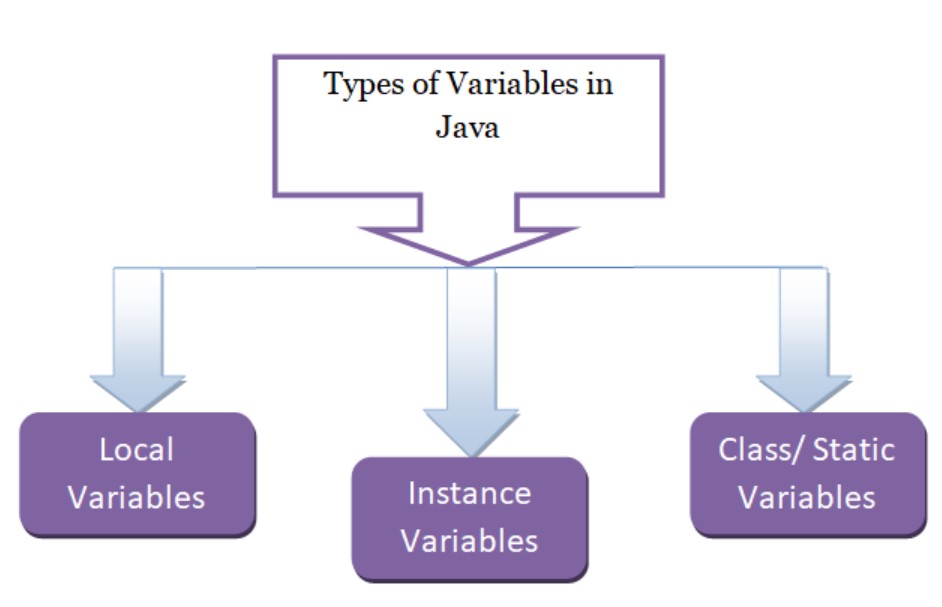
- Local and Instance Variables:
public class Person {
// Instance variables
String name;
int age;
// Constructor
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name; // "this" refers to the instance of the class
this.age = age;
}
// Method using instance variables
public void printInfo() {
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Age: " + age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Local variables
Person person1 = new Person("Alice", 25);
Person person2 = new Person("Bob", 30);
person1.printInfo();
person2.printInfo();
}
}
In the last example, we see the use of both local variables (inside methods) and instance variables (belonging to a class). Instance variables are associated with objects created from the class, while local variables are defined within methods and have limited scope.