Webserver Security
Web server security is crucial to protect your web applications and data from various threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
Some key aspects and best practices for enhancing web server security:
-
Regular Software Updates: Keep your web server software, operating system, and all installed software up to date. Security patches are often released to address vulnerabilities. Automated updates can help in this regard.
-
Firewall Configuration: Implement a firewall to control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Configure the firewall to allow only necessary traffic to reach your web server.
-
Secure Protocols: Use secure protocols like HTTPS (TLS/SSL) to encrypt data in transit. Secure your server's SSL/TLS configuration and regularly update certificates.
-
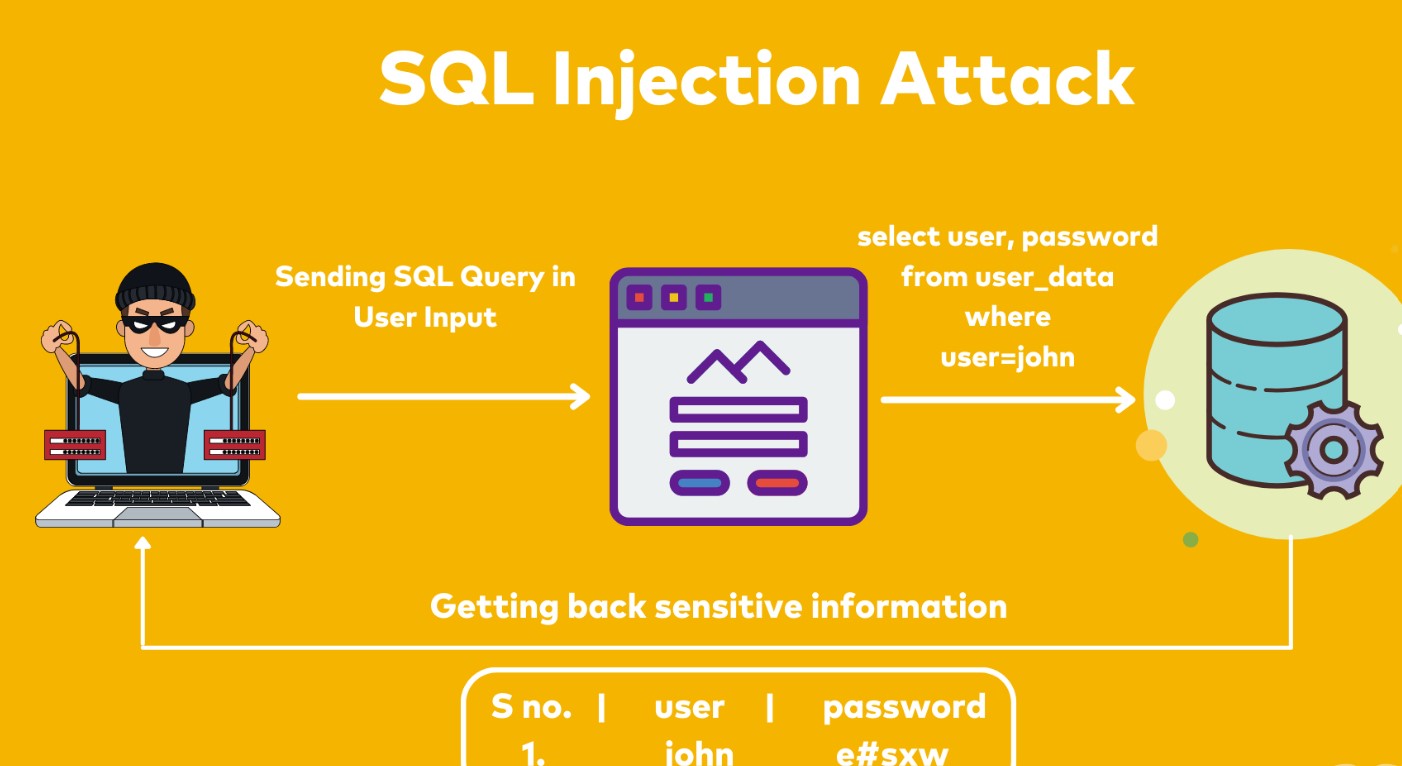
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Deploy a WAF to filter and monitor incoming web traffic for malicious requests and to protect against various web application attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
-
Access Control: Employ strong access control mechanisms. Limit access to the server through secure authentication and authorization. Use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible.
-
File and Directory Permissions: Restrict file and directory permissions on the server to ensure that only authorized users or processes can access, modify, or execute them. Regularly review and audit file permissions.
-
Security Headers: Implement security HTTP headers, such as Content Security Policy (CSP), HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), and X-Content-Type-Options, to mitigate various web vulnerabilities.
-
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Utilize IDS and IPS tools to detect and prevent intrusions. These systems can monitor server activity for unusual behavior and block suspicious traffic.
-
Security Patches and Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your web server for known vulnerabilities and apply patches promptly. Vulnerability scanning tools can help identify potential weaknesses.
-
Security Plugins and Modules: Depending on your web server software, consider using security plugins or modules specifically designed for enhancing security. For example, ModSecurity for Apache.
-
Log Management: Enable and regularly review logs, including access logs, error logs, and security logs. Log analysis can help detect and respond to security incidents.
-
DDoS Mitigation: Deploy DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation solutions to protect your server from overwhelming traffic. This may involve using a content delivery network (CDN) or a dedicated DDoS protection service.
-
Backup and Recovery: Implement regular backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure that you can quickly restore your server in case of a compromise or data loss. Store backups securely, and test recovery procedures.
-
Security Headers: Use security headers, such as Content Security Policy (CSP), HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), and X-Content-Type-Options, to enhance protection against common web security vulnerabilities.
-
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your web server setup. Address the issues discovered during these assessments.
-
Security Training: Ensure that your staff responsible for managing the web server are trained in security best practices. Human error can be a significant security risk.
-
Restrictive Upload Policies: If your web application allows file uploads, ensure strict policies are in place to prevent malicious file uploads and execution. Restrict file types and scan uploads for malware.
-
Web Server Isolation: If feasible, isolate your web server from other critical infrastructure components. Use separate servers for different services and applications to limit the impact of a security breach.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to respond to security incidents effectively. Ensure that all staff are aware of the plan and their roles during an incident.
Web server security is an ongoing process. It's essential to stay informed about emerging threats and best practices and regularly monitor and update your security measures to protect your server and the data it hosts.