Application Programming Interface
An Application Programming Interface (API) is a set of rules and protocols that allows one software application to interact with another. It defines how different software components should communicate, specifying the methods and data formats they should use.
APIs play a crucial role in modern software development by enabling the integration of different systems, applications, or services. They provide a standardized way for developers to access the functionality of a software component without needing to understand its internal workings.
This abstraction allows for the creation of more complex and feature-rich applications by leveraging the capabilities of existing software.
Some key points about APIs:
-
Communication Bridge: APIs act as a bridge between different software components, allowing them to exchange information and perform actions.
-
Standardization: APIs establish a standard set of rules for communication, making it easier for developers to understand and use the functionality provided by a service or library.
-
Reusability: APIs promote code reusability by allowing developers to use existing functionality without having to rewrite the entire codebase. This saves time and resources.
-
Interoperability: APIs enable different software systems, regardless of their underlying technologies or programming languages, to work together. This is essential for creating integrated and interconnected applications.
-
Abstraction: APIs abstract the complexity of underlying systems, providing a simplified interface that developers can interact with. This abstraction shields developers from the internal details of the software they are interacting with.
-
Types of APIs: There are various types of APIs, including:
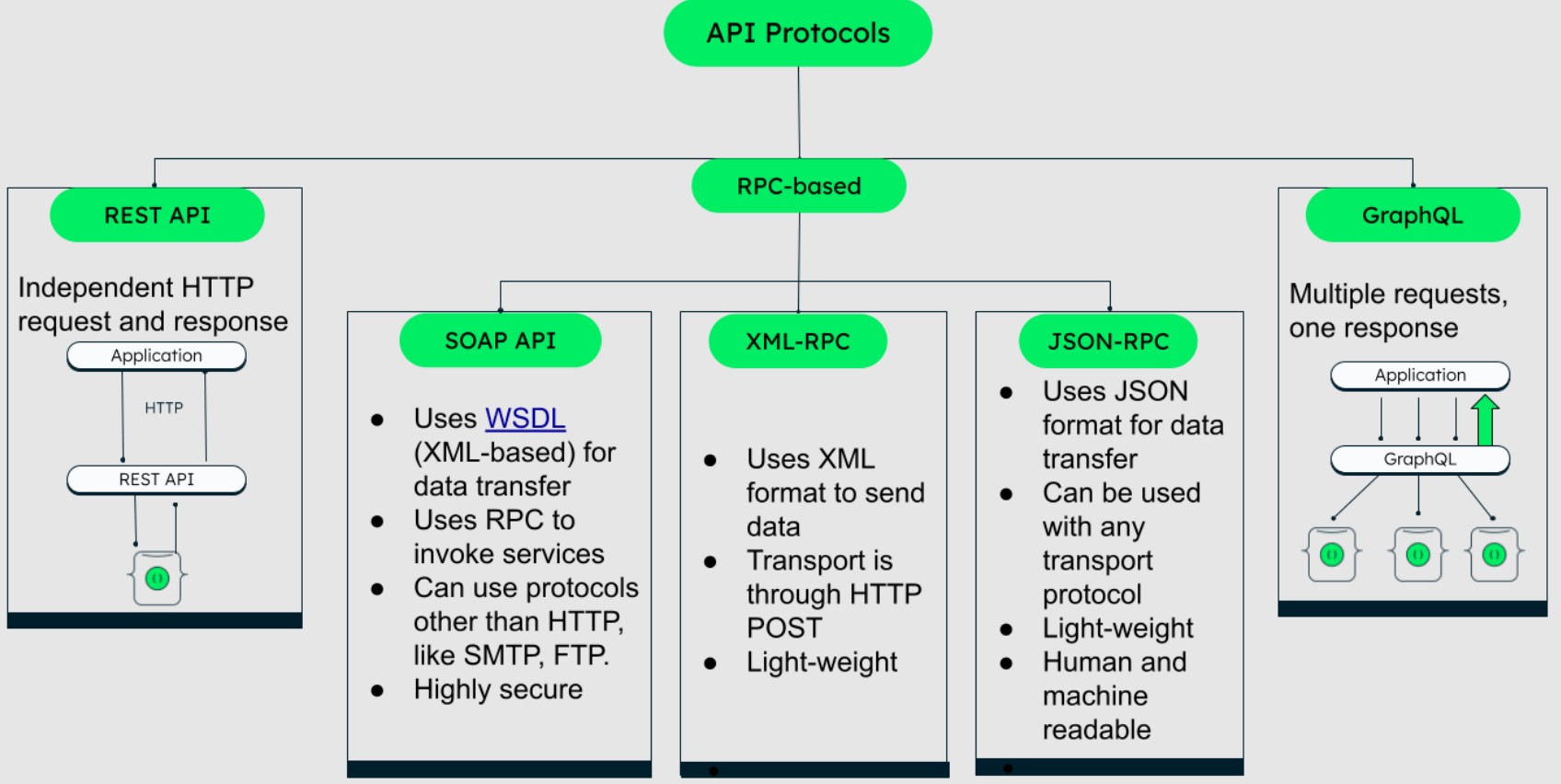
- Web APIs: Used for communication over the internet, often following protocols like HTTP. REST (Representational State Transfer) and SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) are common web API styles.
- Library APIs: Provide a set of functions and procedures that can be used by applications.
- Operating System APIs: Allow applications to interact with the underlying operating system's functionality.
-
Documentation: APIs come with documentation that describes how to use them, including details about available endpoints, methods, parameters, and response formats.
-
Security: APIs often include mechanisms for authentication and authorization to ensure that only authorized users or applications can access certain functionalities.
In summary, an API serves as a contract between different software components, facilitating communication and enabling the building of more robust and feature-rich applications. APIs are fundamental to the development of modern software systems and are used in various domains, including web development, mobile app development, cloud computing, and more.
What is an API?
- An API, short for Application Programming Interface, is a software intermediary that allows two applications to talk to each other and exchange data.
- It acts as a messenger, taking requests from one application and delivering responses from another.
- It serves as a bridge between different software components, enabling them to interact and share information in a structured way.
How APIs Work:
- Request: A client application (like a website, mobile app, or another software program) initiates a request to an API, specifying the desired data or action.
- Communication: The request is sent to the API server, typically over the internet using the HTTP protocol.
- Processing: The API server processes the request, interacting with databases, performing calculations, or accessing other resources as needed.
- Response: The API server constructs a response, often in a structured format like JSON or XML, and sends it back to the client application.
- Delivery: The client application receives the response and processes it accordingly, displaying data to the user, integrating it with other parts of the application, or triggering further actions.
Key Benefits of APIs:
- Data sharing and integration: Facilitate seamless data exchange between different applications, even if they're built by different companies or use different technologies.
- Innovation and efficiency: Allow developers to build new features and apps without having to recreate existing functionality from scratch, saving time and resources.
- Expanding reach and capabilities: Enable businesses to expose their data and services to a wider audience, creating new opportunities for partnership and growth.
- Customization and personalization: Can be used to tailor experiences for individual users, providing relevant content and features based on their preferences and needs.
Types of APIs:
- REST APIs: The most common type, using HTTP requests to access and manipulate data.
- SOAP APIs: An older protocol, often used in enterprise applications.
- GraphQL APIs: A newer query language that allows for more flexible data retrieval.
Common Examples of APIs in Use:
- Checking the weather on a phone app
- Making payments online
- Booking flights or hotels
- Sharing posts on social media
- Integrating maps into apps
- Sending text messages or emails from apps
- Accessing cloud storage services
- Using voice assistants
- And many more!
APIs play a crucial role in modern software development, powering the interconnected digital world we live in. They enable seamless communication between applications, streamline development processes, and drive innovation across industries.