SSL/TLS Overview
What is SSL/TLS?
- Stands for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- Protocols that create secure connections between web browsers and servers
- Protect sensitive information like credit card numbers, passwords, and personal data
SSL/TLS Overview:
-
Purpose:
- SSL/TLS protocols provide a secure channel for data transmission over the internet.
- They ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authentication of data exchanged between systems.
-
Versions:
- SSL and TLS have different versions (SSL 1.0, SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3). It's crucial to use the latest version for security reasons.
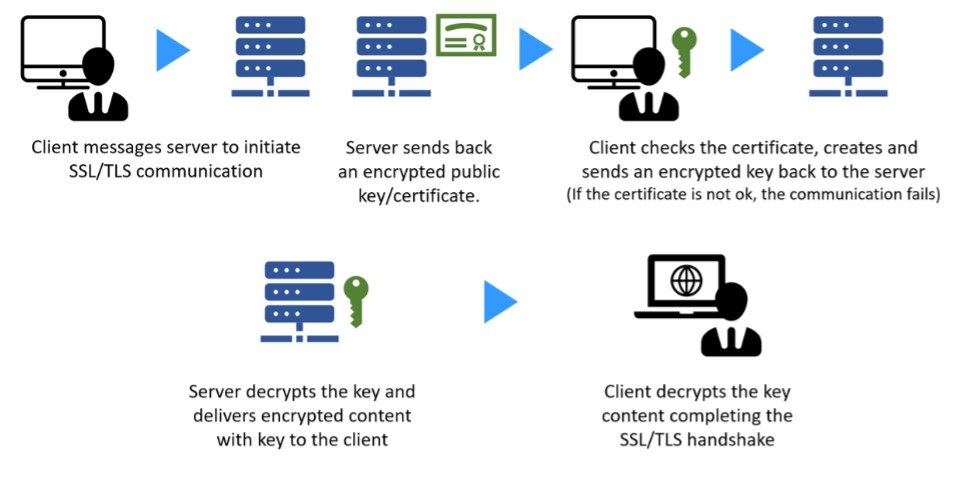
How does SSL/TLS work?
-
Handshake Process:
- ClientHello: Initiates the connection, indicating supported cryptographic algorithms.
- ServerHello: Responds with selected algorithms and a digital certificate.
- Key Exchange: Establishes a shared secret key between the client and server.
- Finished: Both parties confirm the handshake is complete.
-
Encryption:
- SSL/TLS use symmetric and asymmetric cryptography.
- Symmetric encryption is used for data transmission, and asymmetric encryption is used for key exchange and authentication.
-
Certificates:
- Digital certificates are used to verify the identity of parties involved.
- Certificates are issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs).
- The X.509 standard defines the format of certificates.
-
Cipher Suites:
- A cipher suite is a set of cryptographic algorithms used for key exchange, encryption, and message authentication.
- It includes algorithms for key exchange, encryption, and MAC (Message Authentication Code).