Operating System (OS)
An operating system (OS) is a software component that acts as an intermediary between computer hardware and the user.
It provides a platform for software applications to run and manages computer hardware resources.
Overview of the key functions and components of an operating system:
Kernel:
- The core component of the operating system.
- Manages hardware resources such as CPU, memory, disk I/O, and peripheral devices.
- Provides essential services for other parts of the operating system and user applications.
Process Management:
- Manages the creation, scheduling, and termination of processes (instances of executing programs).
- Allocates resources to processes and ensures their efficient execution.
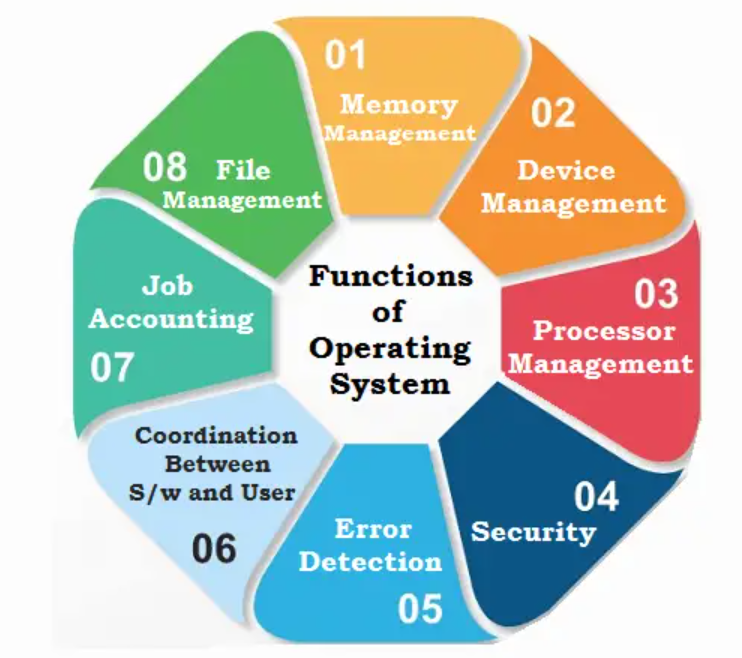
Memory Management:
- Manages the system's memory, including RAM and virtual memory.
- Allocates and deallocates memory space for processes.
- Implements techniques like paging and segmentation for efficient memory usage.
File System:
- Manages files on storage devices (hard drives, SSDs, etc.).
- Provides a hierarchical structure for organizing and storing files and directories.
- Implements file permissions and access control.
Device Drivers:
- Enables communication between the operating system and hardware devices.
- Acts as an interface for input/output operations with devices such as printers, graphics cards, and network interfaces.
User Interface:
- Provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with the computer.
- Types of interfaces include Command-Line Interface (CLI), Graphical User Interface (GUI), and increasingly, touch-based or voice-controlled interfaces.
Security:
- Implements security measures to protect the system and user data.
- Includes user authentication, access control, encryption, and firewall functionalities.
Networking:
- Manages network connections and communication.
- Implements protocols for data transfer over networks (TCP/IP, UDP).
- Facilitates the configuration of network settings.
System Calls:
- Provides an interface between applications and the kernel.
- Applications use system calls to request services from the operating system.
Utilities:
- Collection of system utilities and tools for managing and maintaining the system.
- Examples include text editors, file managers, and diagnostic tools.
Boot Process:
- The sequence of steps the computer follows to load the operating system into memory and start the system.
- Involves activities like Power-On Self-Test (POST) and loading the bootloader.
Multiuser and Multitasking:
- Supports multiple users and allows concurrent execution of multiple processes.
- Time-sharing systems enable efficient sharing of resources among users.
Error Handling:
- Manages errors and exceptions that may occur during system operation.
- Provides mechanisms for logging and reporting errors.
Updates and Maintenance:
- Supports system updates and maintenance tasks.
- Can include patching the OS, updating drivers, and installing software.
Virtualization:
- Allows the creation of virtual environments (virtual machines or containers) on a single physical machine.
- Facilitates resource isolation and efficient utilization.
Common Types of Operating Systems:
- Desktop OS: Windows, macOS, Linux
- Mobile OS: Android, iOS
- Server OS: Windows Server, Linux (e.g., Ubuntu Server, CentOS)
- Embedded OS: Used in devices like smartwatches, appliances
- Real-time OS: Used in time-critical systems like medical equipment
Operating System (OS)
Enroll Now
- Computer Science
- Machine Learning