SQL Join Statement
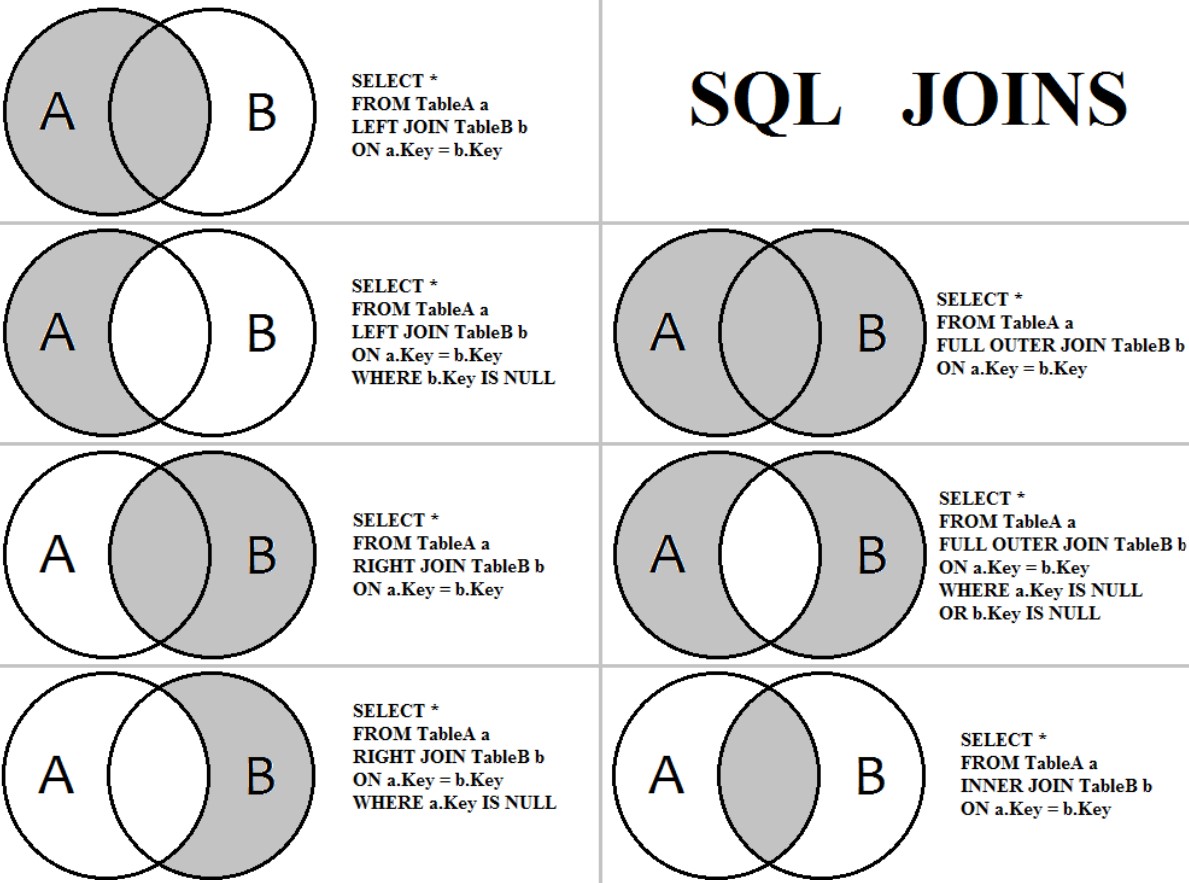
In SQL, the JOIN statement is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. It allows you to retrieve data from multiple tables in a single query by specifying how the tables are related.
The most common types of joins are INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN), RIGHT JOIN (or RIGHT OUTER JOIN), and FULL JOIN (or FULL OUTER JOIN).
Let's walk through some SQL JOIN statements with examples using two hypothetical tables: orders and customers. The orders table contains information about customer orders, and the customers table contains customer information.
Here are the structures of these two tables:
orders Table:
| order_id | customer_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | 2023-01-15 |
| 2 | 102 | 2023-01-18 |
| 3 | 101 | 2023-01-20 |
| 4 | 103 | 2023-01-22 |
customers Table:
| customer_id | customer_name | country |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Alice Johnson | USA |
| 102 | Bob Smith | Canada |
| 103 | Carol Williams | UK |
| 104 | David Lee | Australia |
Now, let's perform various SQL JOIN operations:
-
INNER JOIN:
An INNER JOIN retrieves rows from both tables where there is a matching
customer_id.SELECT orders.order_id, customers.customer_name FROM orders INNER JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id;Result:
order_id customer_name 1 Alice Johnson 2 Bob Smith 3 Alice Johnson 4 Carol Williams Explanation: This query combines data from both the
ordersandcustomerstables, showing theorder_idandcustomer_namefor each order. -
LEFT JOIN (LEFT OUTER JOIN):
A LEFT JOIN retrieves all rows from the
orderstable and matching rows from thecustomerstable. If there's no match in thecustomerstable, it still includes the order.SELECT orders.order_id, customers.customer_name FROM orders LEFT JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id;Result:
order_id customer_name 1 Alice Johnson 2 Bob Smith 3 Alice Johnson 4 Carol Williams NULL David Lee Explanation: This query includes all orders from the
orderstable, even if there is no matching customer in thecustomerstable (e.g., order withcustomer_id104). -
RIGHT JOIN (RIGHT OUTER JOIN):
A RIGHT JOIN retrieves all rows from the
customerstable and matching rows from theorderstable. If there's no match in theorderstable, it still includes the customer.SELECT orders.order_id, customers.customer_name FROM orders RIGHT JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id;Result:
order_id customer_name 1 Alice Johnson 2 Bob Smith 3 Alice Johnson 4 Carol Williams Explanation: This query includes all customers from the
customerstable and their corresponding orders, if any. -
FULL JOIN (FULL OUTER JOIN):
A FULL JOIN retrieves all rows from both tables and combines them. It includes all orders and all customers, with NULL values where there's no match.
SELECT orders.order_id, customers.customer_name FROM orders FULL JOIN customers ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id;Result:
order_id customer_name 1 Alice Johnson 2 Bob Smith 3 Alice Johnson 4 Carol Williams NULL David Lee Explanation: This query combines all orders and all customers, showing NULL values where there's no match.
These examples demonstrate how SQL JOIN statements can be used to combine data from multiple tables based on related columns, allowing you to retrieve and analyze data from a relational database effectively.
Enroll Now
- SQL
- DBMS