Best DevOps Tools in 2024
DevOps is a set of practices, principles, and cultural philosophies that aim to streamline and integrate the processes between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). The primary goal of DevOps is to shorten the software development lifecycle, increase the frequency of software releases, and improve the quality and reliability of software applications
The DevOps landscape is constantly evolving, with new tools and platforms emerging all the time.The top DevOps tools in 2024 will likely be a mix of existing and emerging technologies.
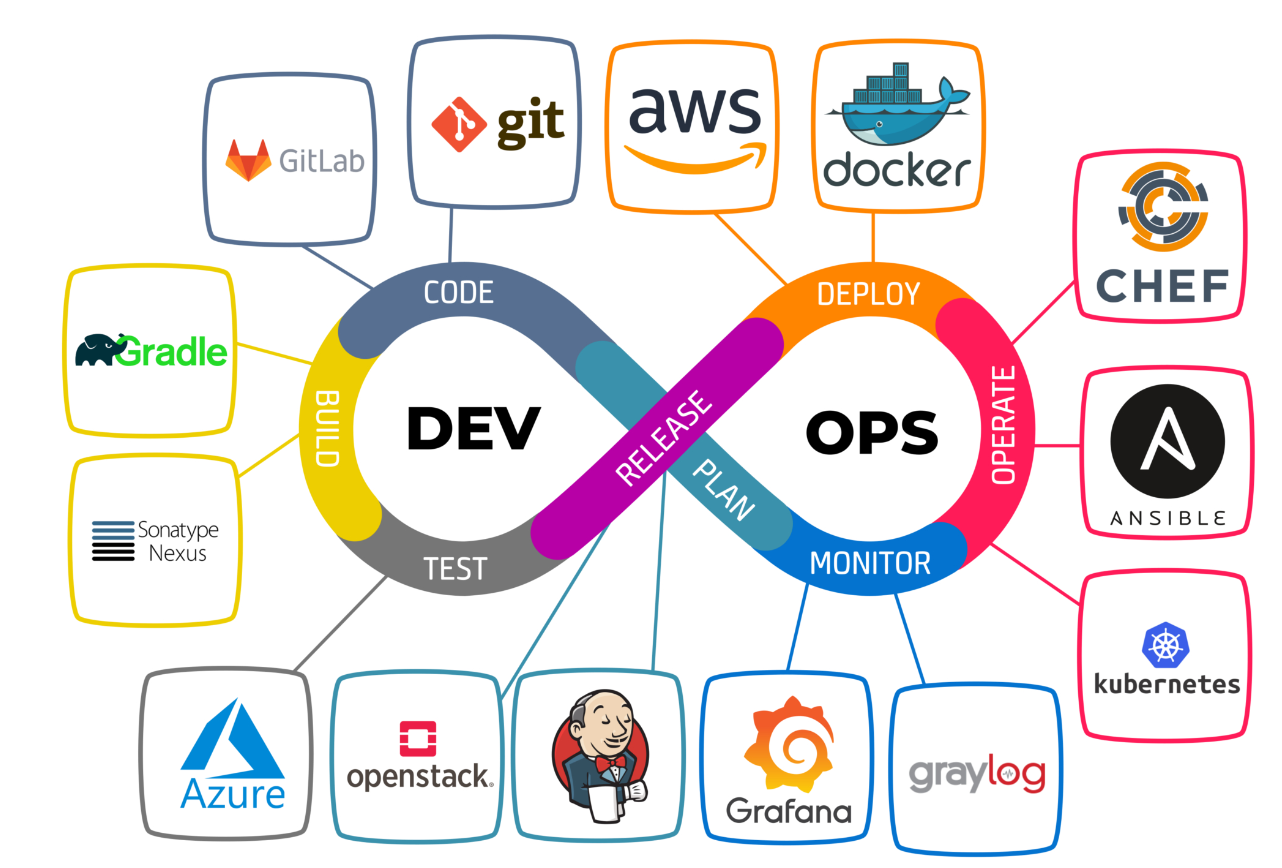
Some popular DevOps tools across various categories
-
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
- Jenkins: An open-source automation server widely used for building, testing, and deploying software.
- GitLab CI/CD: Integrated CI/CD capabilities within the GitLab platform, providing version control, CI, CD, and container registry.
- CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD platform that automates software development processes.
- GitHub Actions: Allows automating workflows directly within GitHub repositories for CI/CD and other tasks.
-
Configuration Management:
- Ansible: An open-source automation tool for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation.
- Puppet: A configuration management tool for managing the configuration of servers at scale.
- Chef: A powerful automation platform that transforms infrastructure into code.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
- Terraform: An open-source tool for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure safely and efficiently.
- AWS CloudFormation: Provides a way to create and manage a collection of related AWS resources.
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Templates: Allows defining the infrastructure and dependencies for Azure solutions in code.
-
Containerization and Orchestration:
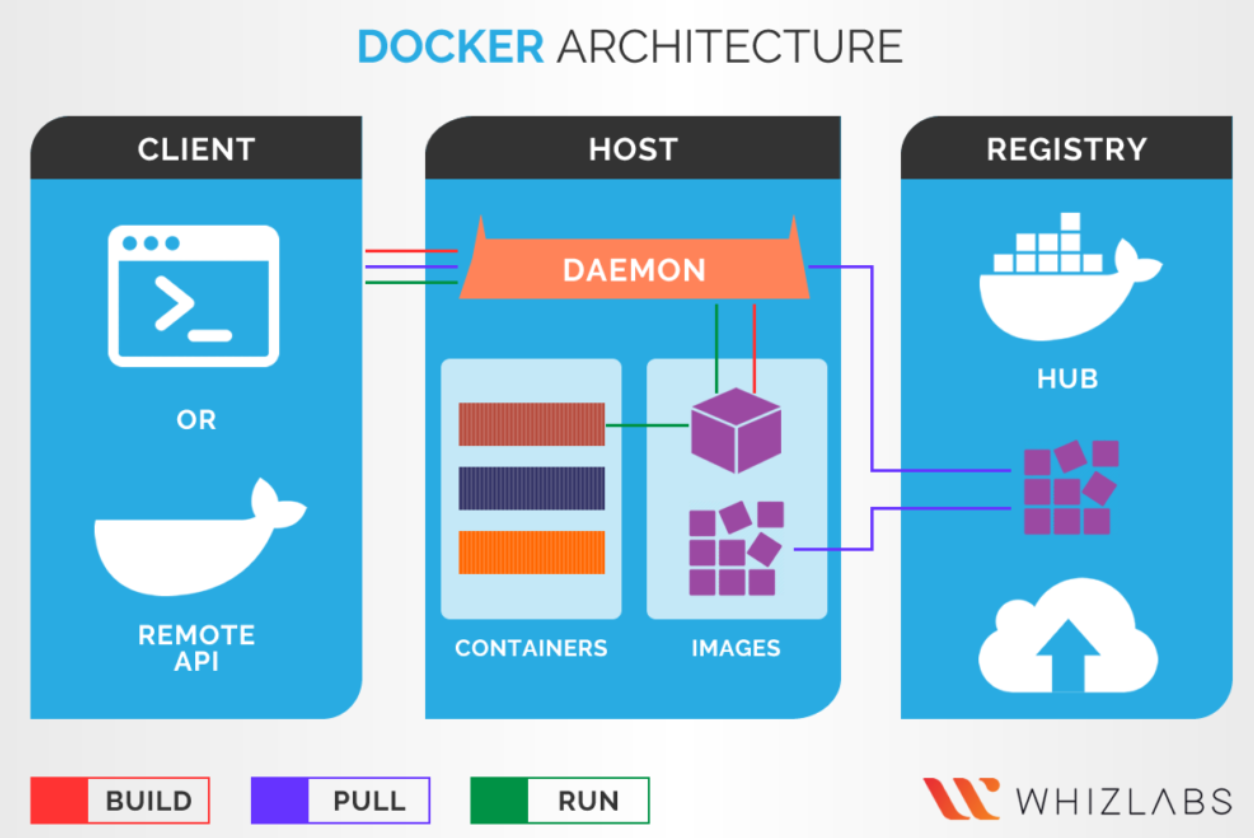
- Docker: A platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers.
- Kubernetes: An open-source container orchestration platform for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- Red Hat OpenShift: A Kubernetes-based platform for container orchestration and management.
-
Monitoring and Logging:
- Prometheus: An open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit designed for reliability and scalability.
- Grafana: An open-source analytics and monitoring platform that allows querying, visualizing, and alerting on metrics.
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): A set of tools for centralized logging, log processing, and visualization.
-
Collaboration and Communication:
- Slack: A popular collaboration platform for teams, offering channels, messaging, and integrations with other tools.
- Microsoft Teams: Provides chat, video meetings, file sharing, and integrations with Microsoft 365 apps.
- Mattermost: An open-source, self-hosted messaging platform with features similar to Slack.
-
Version Control:
- Git: The most widely used distributed version control system for tracking changes in source code during software development.
- GitHub: A web-based platform for hosting and collaborating on Git repositories, offering features like pull requests, code review, and issue tracking.
- GitLab: A web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides Git repository management, CI/CD, and collaboration features.
Principles of DevOps
-
Collaboration: DevOps emphasizes collaboration and communication between development, operations, and other relevant teams. This reduces silos and enhances the flow of information.
-
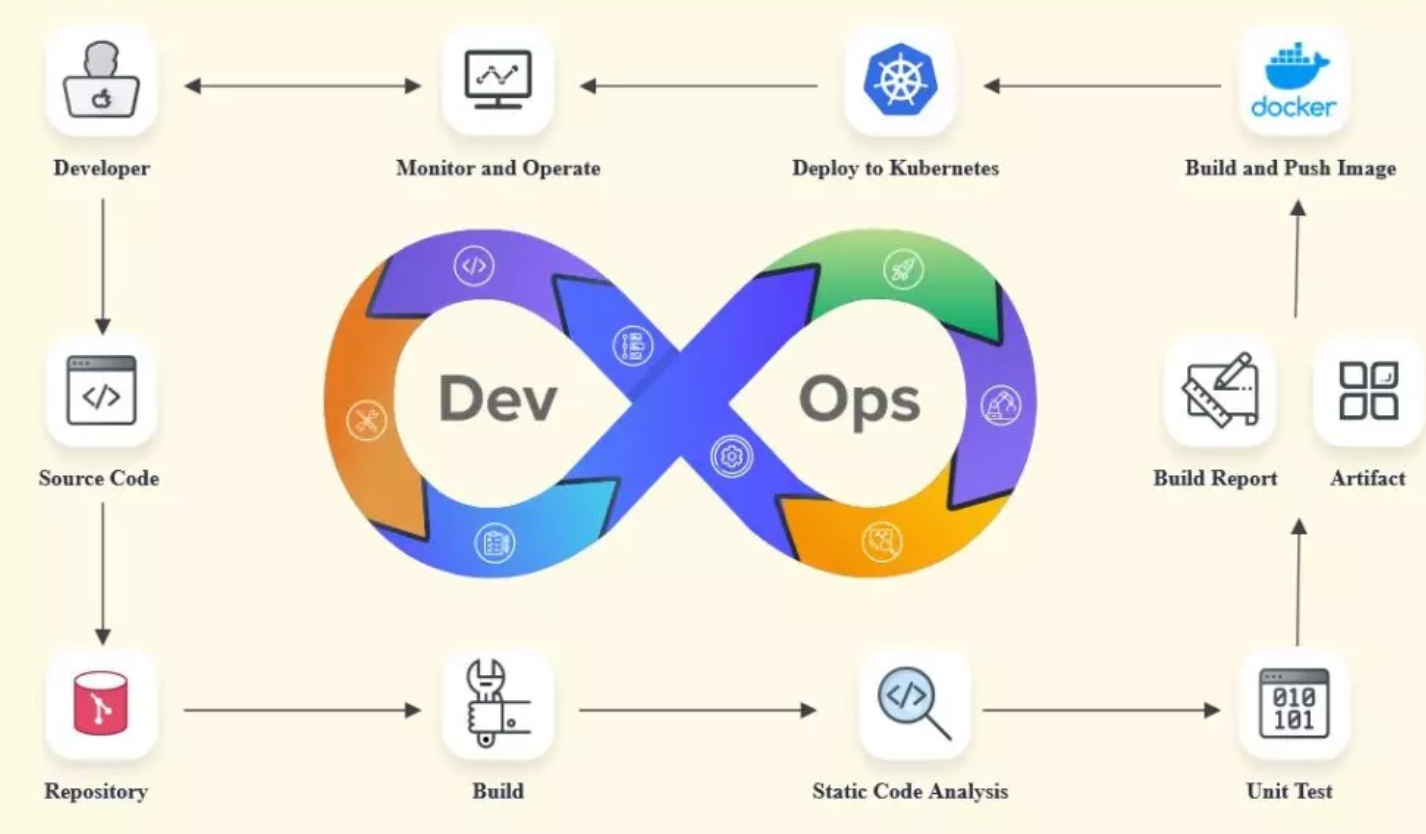
Automation: Automation is a core aspect of DevOps. It involves automating repetitive tasks such as building, testing, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning. This increases efficiency, reduces errors, and speeds up the development process.
-
Continuous Integration (CI): CI involves frequently integrating code changes from developers into a shared repository. Automated tests are run to ensure that the changes don't introduce defects. CI aims to catch integration issues early in the development cycle.
-
Continuous Delivery (CD): CD takes CI a step further by automatically deploying code changes to staging or production environments after passing automated tests. This ensures that software is always in a deployable state, making releases smoother and more reliable.
-
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC involves managing and provisioning infrastructure (servers, networks, etc.) using code and automation tools. This ensures consistent and repeatable infrastructure setup, reducing manual configuration and potential errors.
-
Microservices: Microservices architecture involves breaking down an application into smaller, loosely coupled services that can be developed, deployed, and maintained independently. This allows for more flexibility and scalability.
-
Monitoring and Feedback: Continuous monitoring of applications and infrastructure helps identify issues and performance bottlenecks. Feedback loops ensure that developers and operations teams can make improvements based on real-time data.
-
Security: DevOps integrates security practices throughout the software development lifecycle, known as DevSecOps. Security is not an afterthought but an integral part of the development process.
-
Version Control: Version control systems, such as Git, enable teams to manage and track changes to code and other project assets. This facilitates collaboration, rollbacks, and traceability.
-
Agile and Lean Practices: DevOps aligns well with Agile and Lean methodologies by promoting iterative development, customer feedback, and a focus on delivering value quickly.
Benefits of DevOps
-
Faster Time to Market: DevOps practices enable faster development cycles and quicker deployment of features, leading to faster time-to-market for products.
-
Improved Quality: Automation and continuous testing result in higher-quality code with fewer defects and faster bug identification.
-
Increased Collaboration: DevOps breaks down communication barriers between teams, leading to better collaboration and shared responsibility.
-
Greater Efficiency: Automation reduces manual tasks, which saves time and minimizes human errors.
-
Enhanced Scalability: DevOps practices make it easier to scale applications and infrastructure to meet demand.
-
Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback loops help teams continuously improve their processes and products.
-
Reliability: Automated deployment and monitoring improve the reliability of applications and services.
Learn more about DevOps optimization with janaai
- EasySolveAI Blog
- Machine Learning