Shell Scripting Tutorial
Shell scripting is a powerful way to automate tasks and perform various operations in a Unix-like environment. In this tutorial, I'll provide you with a basic introduction to shell scripting. We'll focus on the Bash shell, which is the default shell on most Linux distributions and macOS.A shell script is a plain text file that contains a sequence of shell commands. These commands are executed in order when you run the script. Shell scripts are useful for automating repetitive tasks, managing system configurations, and performing various operations on files and data.
Creating a Shell Script
To create a shell script, you'll need a text editor (e.g., nano, vim, or gedit). Here's how to create a basic shell script:
- Open your text editor.
- Create a new file with a
.shextension (e.g.,myscript.sh). - Add the following line at the beginning of your script to specify the shell to use (Bash, in this case):
#!/bin/bash - Write your shell commands below this line.
Making the Script Executable
Before you can run a shell script, you need to make it executable. Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where your script is located. Use the chmod command to add execute permissions:
chmod +x myscript.sh
Running the Script
To execute your script, simply run it from the terminal:
./myscript.sh
Basic Script Example
Here's a simple script that prints "Hello, World!" to the terminal:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, World!
Variables
You can use variables in shell scripts to store and manipulate data:
#!/bin/bash
name="John"
echo "Hello, $name!
User Input
You can read user input using the read command:
#!/bin/bash
echo -n "Enter your name: "
read name
echo "Hello, $name!
Conditional Statements
You can use if statements for conditional execution:
#!/bin/bash
age=25
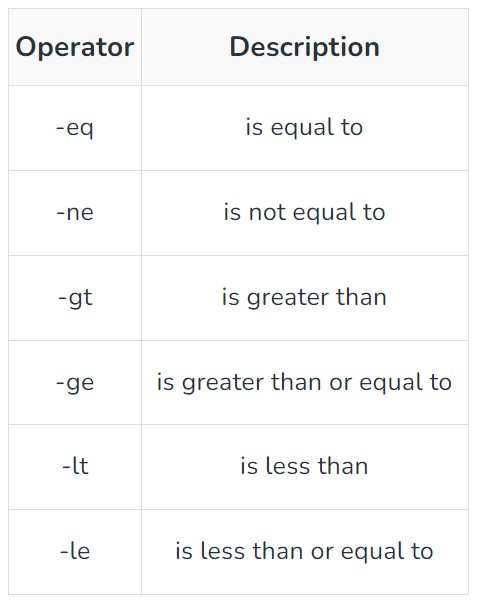
if [ $age -ge 18 ]; then
echo "You are an adult."
else
echo "You are not yet an adult."
fi
Loops
Shell scripts support for and while loops for repetitive tasks:
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..5}; do
echo "Iteration $i"
done
Functions
You can define functions in shell scripts for better organization and code reuse:
#!/bin/bash
function greet() {
echo "Hello, $1!"
}
greet "Alice"
greet "Bob"
File Operations
Shell scripts are often used for file manipulation. You can use commands like ls, cp, mv, and rm to work with files and directories.
Error Handling
You can handle errors using the exit command and error codes. A non-zero exit code typically indicates an error:
#!/bin/bash
if [ ! -f myfile.txt ]; then
echo "File not found."
exit 1
fi
This is a basic introduction to shell scripting. As you become more familiar with shell scripting, you can explore more advanced topics, such as regular expressions, piping, and command-line arguments. Shell scripting is a powerful skill for automating tasks and managing systems in a Unix-like environment.
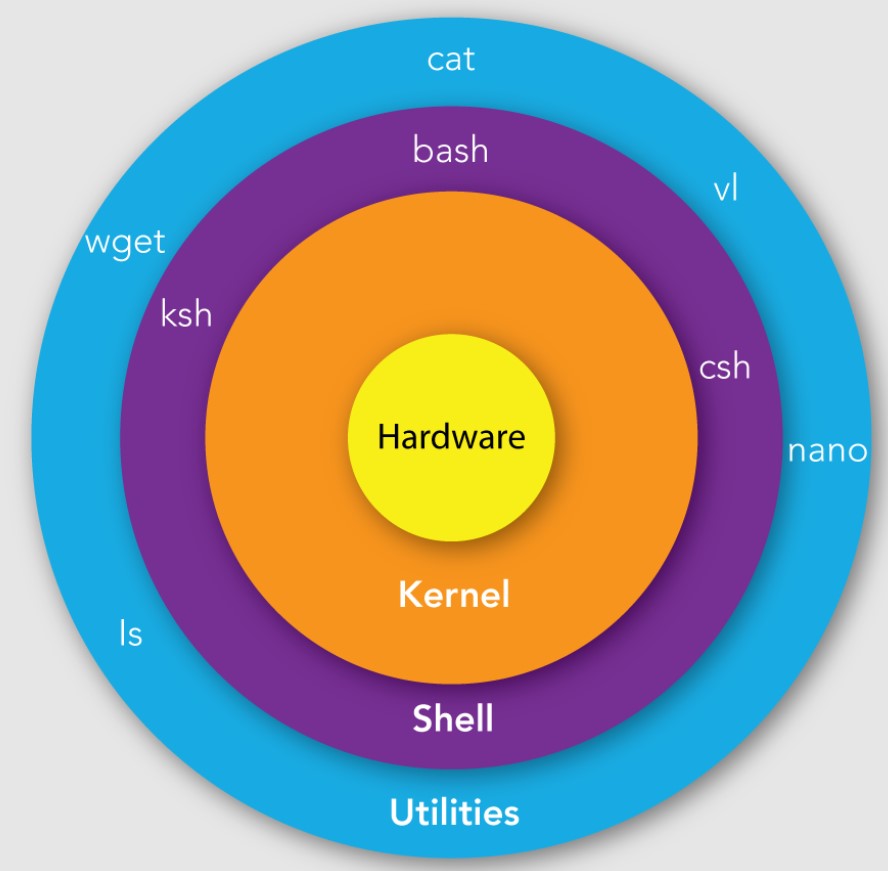
Shell scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks on Unix-like operating systems. Shell scripts are simply text files that contain a list of commands to be executed one by one.To write a shell script, you can use any text editor, such as vi or nano. Once you have written your script, you can save it with a .sh extension. For example, a simple shell script that prints the current date and time to the console might look like this:
#!/bin/bash
echo "The current date and time is: $(date)"
The first line of the script (#!/bin/bash) is called the shebang. It tells the shell which interpreter to use to execute the script. In this case, we are using the Bash shell.
To execute a shell script, you can use the bash command. For example, to execute the script above, you would type the following command:
bash my_script.sh
You can also make a shell script executable by running the following command:
chmod +x my_script.sh
Once a shell script is executable, you can run it by typing the name of the script without the .sh extension. For example, to run the script above, you would type the following command:
./my_script
Shell scripts can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks, such as:
- Backing up files
- Installing software
- Configuring systems
- Performing data analysis
- Running tests
Example of a shell script that backs up all of the files in the current directory to a new directory called backup:
#!/bin/bash
# Create a new backup directory
mkdir backup
# Copy all of the files in the current directory to the backup directory
cp * backup
# Print a message to the console
echo "Backup complete!"
To use this script, you would save it as a file with a .sh extension, such as backup.sh. Then, you could execute the script by running the following command:
./backup.sh

Shell scripting is a powerful tool that can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks. If you are interested in learning more about shell scripting, there are many resources available online and in libraries.
Some additional tips for writing shell scripts:
- Use comments to document your code. This will make your script easier to read and understand.
- Use variables to store data. This will make your script more reusable and easier to maintain.
- Use control flow statements, such as
if,else, andwhileloops, to control the flow of your script. - Use functions to group related code together. This will make your script more modular and easier to test.
- Test your scripts thoroughly before using them in production.
Shell scripting can be a bit tricky to learn at first, but it is a valuable skill to have. With a little practice, you will be able to write shell scripts to automate all sorts of tasks.
Enroll Now
- Shell Programming
- Machine Learning