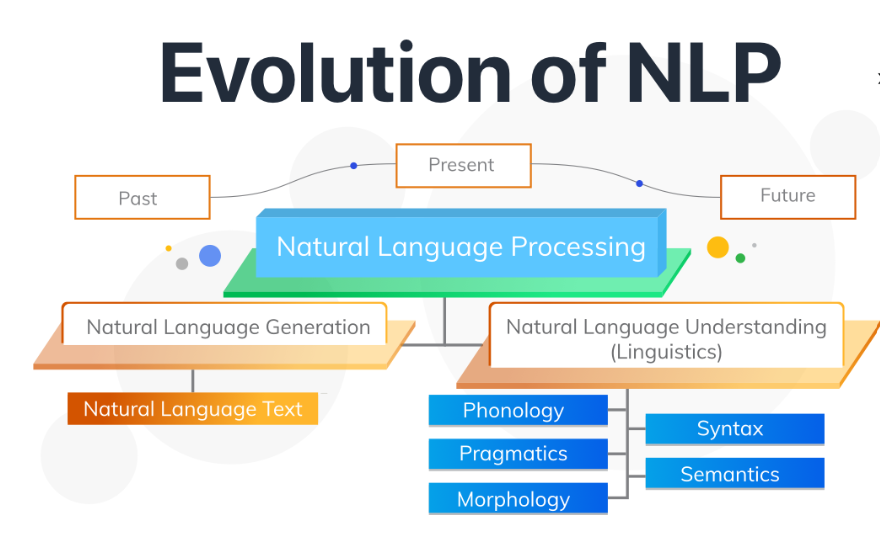
Building blocks of language in natural language processing (NLP)
The building blocks of language in natural language processing (NLP) refer to the foundational components that make up the structure of human languages. These building blocks include phonemes, morphemes, lexemes, syntax, and semantics.
Let's explore each of these building blocks with examples:
-
Phonemes: Phonemes are the smallest distinct units of sound in a language. They are combined to form words. Different languages have different sets of phonemes. For example, in English:
- The words "bat" and "pat" differ only in the initial phoneme /b/ and /p/, respectively.
-
Morphemes: Morphemes are the smallest meaningful units of language. They can be words or parts of words that carry a specific meaning. Morphemes can be prefixes, suffixes, or roots. For example:
- The word "unhappiness" consists of three morphemes: "un-" (prefix), "happy" (root), and "-ness" (suffix).
-
Lexemes: Lexemes are words or groups of words with the same root and related meanings. They share the same core meaning but can have different inflections or grammatical forms. For example:
- The lexeme "run" includes various forms like "run," "running," "ran," "runs."
-
Syntax: Syntax refers to the arrangement of words to create meaningful sentences. It involves the rules governing word order, phrases, clauses, and sentence structure. For example:
- In English syntax, the subject typically comes before the verb in a sentence, as in "She sings."
-
Semantics: Semantics deals with the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It involves understanding the relationships between words and how they convey information. For example:
- The phrase "hot water" refers to water with a high temperature.
These building blocks are essential for understanding and processing language. NLP algorithms and models leverage these building blocks to perform tasks like text classification, sentiment analysis, machine translation, and more.
By analyzing phonemes, morphemes, lexemes, syntax, and semantics, NLP systems can extract meaning and context from text, making them capable of various language-related tasks.
The building blocks of language in natural language processing (NLP) are the smallest units of meaning that can be identified in a language. These building blocks can be words, phrases, or even sentences.
Some of the most common building blocks of language in NLP:
- Phonemes: Phonemes are the smallest units of sound in a language. They are the building blocks of words. For example, the word "cat" is made up of the three phonemes /k/, /æ/, and /t/.
- Morphemes: Morphemes are the smallest units of meaning in a language. They can be words, prefixes, or suffixes. For example, the word "cats" is made up of the morpheme "cat" and the suffix "s". The morpheme "cat" means "a small, furry mammal that is often kept as a pet". The suffix "s" means "more than one".
- Tokens: Tokens are the basic units of text that are processed by NLP systems. They can be words, punctuation marks, or numbers. For example, the sentence "The cat sat on the mat" is made up of the tokens "The", "cat", "sat", "on", and "the".
- Sentences: Sentences are the basic units of communication in a language. They are made up of words and phrases that are grammatically related to each other. For example, the sentence "The cat sat on the mat" is a simple sentence that consists of a subject ("The cat") and a predicate ("sat on the mat").
The building blocks of language are essential for NLP systems to understand and process text. By understanding the building blocks of language, NLP systems can identify the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences.
This allows NLP systems to perform tasks such as machine translation, text summarization, and question answering.
Some examples of how the building blocks of language are used in NLP:
- Machine translation: Machine translation systems use the building blocks of language to identify the meaning of words and phrases in one language and then translate them into another language.
- Text summarization: Text summarization systems use the building blocks of language to identify the main points of a text and then summarize those points in a shorter form.
- Question answering: Question answering systems use the building blocks of language to understand the meaning of a question and then retrieve the information that is needed to answer the question.
The building blocks of language are a fundamental part of NLP. By understanding these building blocks, NLP systems can be more accurate and efficient at performing tasks such as machine translation, text summarization, and question answering.
Enroll Now
- Python Programming
- Machine Learning