Syntactic and Semantic analysis
Syntactic and semantic analysis are two essential components of natural language processing (NLP) that involve understanding the structure and meaning of sentences and text. Let's explore each of these concepts with examples:
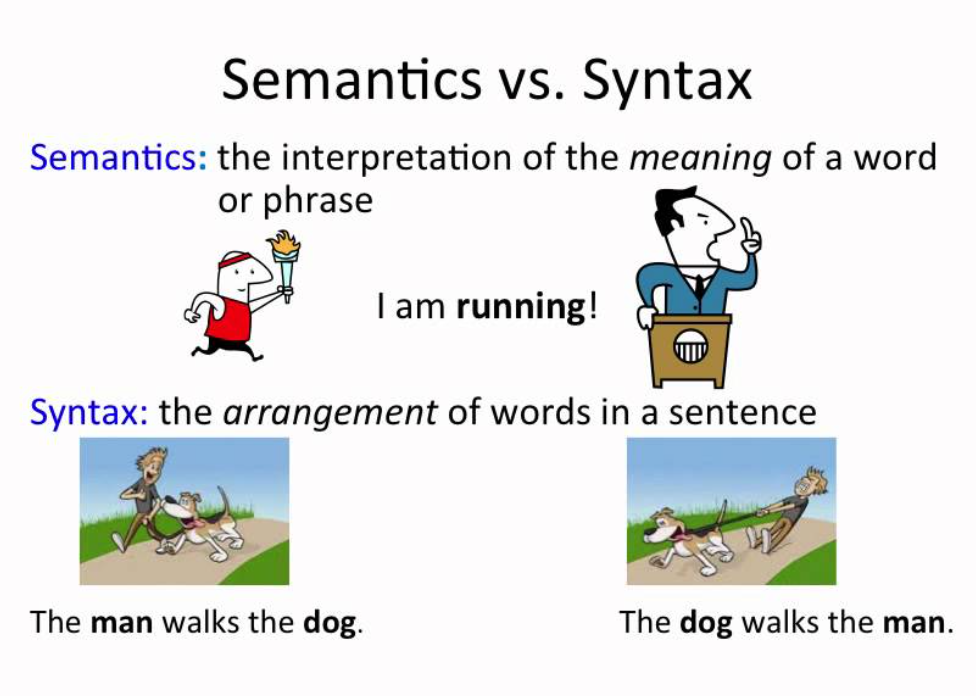
1. Syntactic Analysis: Syntactic analysis, also known as parsing, focuses on analyzing the grammatical structure of sentences to identify the relationships between words and their roles within the sentence. It deals with the arrangement of words and phrases to form well-formed sentences based on the rules of a language's grammar.
Example Sentence: "The cat chased the mouse."
In this sentence, syntactic analysis involves identifying the grammatical roles of the words:
- "The" is a determiner.
- "cat" is a noun, the subject of the sentence.
- "chased" is a verb, the action.
- "the" is a determiner.
- "mouse" is a noun, the direct object of the verb.
Syntactic analysis helps in understanding how words combine to form grammatically valid sentences and provides insights into the sentence's structure.
2. Semantic Analysis: Semantic analysis focuses on understanding the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences in a language. It deals with interpreting the relationships between words and extracting the underlying meaning from text.
Example Sentence: "The cat chased the mouse."
Semantic analysis involves understanding the real-world meaning of the words and their relationships:
- "The cat" is the entity performing the action.
- "chased" indicates a pursuit action.
- "the mouse" is the entity being pursued.
Semantic analysis goes beyond the surface structure to capture the intended meaning of the sentence. It involves resolving word senses, understanding word ambiguity, and identifying relationships between words based on their meaning.
In NLP applications, both syntactic and semantic analysis are crucial for various tasks:
- Sentiment analysis relies on syntactic analysis to identify the structure of sentences and semantic analysis to understand the sentiment conveyed.
- Machine translation uses both analyses to ensure accurate translation while maintaining proper grammar and meaning.
- Question answering systems leverage syntactic and semantic understanding to generate accurate and relevant responses.
In summary, syntactic analysis focuses on the grammatical structure of sentences, while semantic analysis delves into the meaning and relationships between words and phrases. Both analyses contribute to the overall understanding of text and enable NLP systems to perform a wide range of tasks effectively.
Enroll Now
- Python Programming
- Machine Learning