Morphological analysis
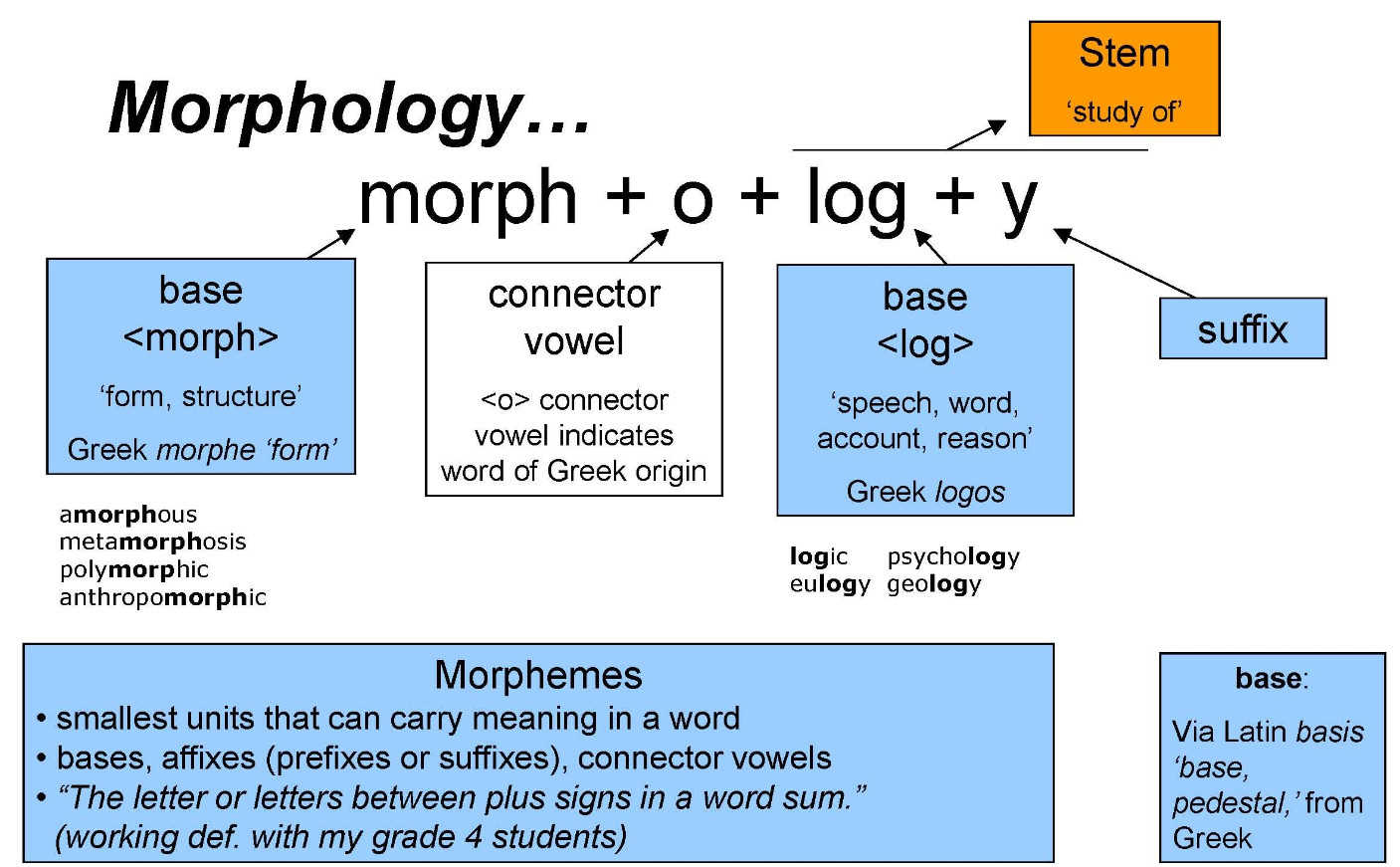
Morphological analysis is a fundamental aspect of natural language processing (NLP) that involves breaking down words into their smallest meaningful units, called morphemes. Morphemes are the smallest grammatical units of a language that carry meaning. Morphological analysis involves understanding how words are formed, including their prefixes, suffixes, roots, and inflections.
Let's explore morphological analysis with an example:
Example Word: "Unhappiness"
In morphological analysis, the word "unhappiness" can be broken down into morphemes:
- "un-" is a prefix indicating negation or reversal.
- "happy" is the root word.
- "-ness" is a suffix indicating a state or quality.
So, the morphological breakdown of "unhappiness" would be:
- Prefix: "un-"
- Root: "happy"
- Suffix: "-ness"
By analyzing the morphological structure of words, NLP systems can gain insights into their meanings, relationships, and grammatical properties. Morphological analysis is especially valuable in languages with rich inflectional systems, where different morphemes indicate tense, gender, number, and other grammatical features.
Morphological analysis is used in various NLP tasks:
- Lemmatization: Identifying the base form (lemma) of a word.
- Stemming: Reducing words to their root form by removing prefixes and suffixes.
- Language generation: Constructing new words based on morphological rules.
- Information retrieval: Handling word variations in search queries.
In languages like English, morphological analysis may seem relatively straightforward, but in languages with complex inflectional systems, such as Arabic or Turkish, morphological analysis becomes a crucial step for accurate NLP tasks.
Overall, morphological analysis provides a deeper understanding of the structure of words, allowing NLP systems to process and interpret language more effectively.
Enroll Now
- Python Programming
- Machine Learning